JWT Keys¶
Document Metadata
Category: Setup & Configuration → Integrations → JWT Keys/Tokens
Audience: Administrators, Engineers, Support Team
Difficulty: Intermediate to Advanced
Time Required: 15–30 minutes
Prerequisites: ConnexCS account with Integrations permissions, understanding of JSON Web Tokens (JWT)
Related Topics: API Integrations (for token usage), OAuth Session (JWT as part of token flows)
Next Steps: OAuth Session, API Usage Guide
Setup Integrations JWT Keys
Introduction¶
JSON Web Tokens (JWT) are widely used in modern web applications for securely transmitting information between client and server.
One of the core elements of JWT is the Refresh Token, which plays a key role in ensuring seamless user sessions while improving security.
Click here for more information on JWT.
What are JWT Keys?¶
JWT Keys are used to extend the validity of a user session without requiring the user to re-enter credentials.
This process involves two tokens:
-
Access Token: This token is generated after a user successfully logs in and is used to authenticate requests. It has a short expiration time (e.g., 30 minutes or 1 hour).
-
Refresh Token: This token is used to request a new access token after the previous one expires, allowing the user to stay logged in for a longer period. The refresh token has a longer expiration time (e.g., 30 days).
How JWT Works?¶
-
User Login:
a. The user enters credentials. For example, the username and password.
b. The system generates an Access Token and a Refresh Token. You can now issue access tokens.
c. The Access Token is short-lived and used to authenticate API requests.
-
Token Expiry:
a. When the Acess Token expires, the client can send the Refresh Token to request a new Access Token.
b. The system validates the Refresh Token and, if valid, generates a new Access Token.
-
Revoke Token: If necessary, the Refresh Token can be revoked to prevent further use. This is typically done in cases where the user logs out, or the system detects a security issue.
How to Add the JWT Keys?¶
- Login to your account.
- Navigate to Setup Integrations JWT Keys.
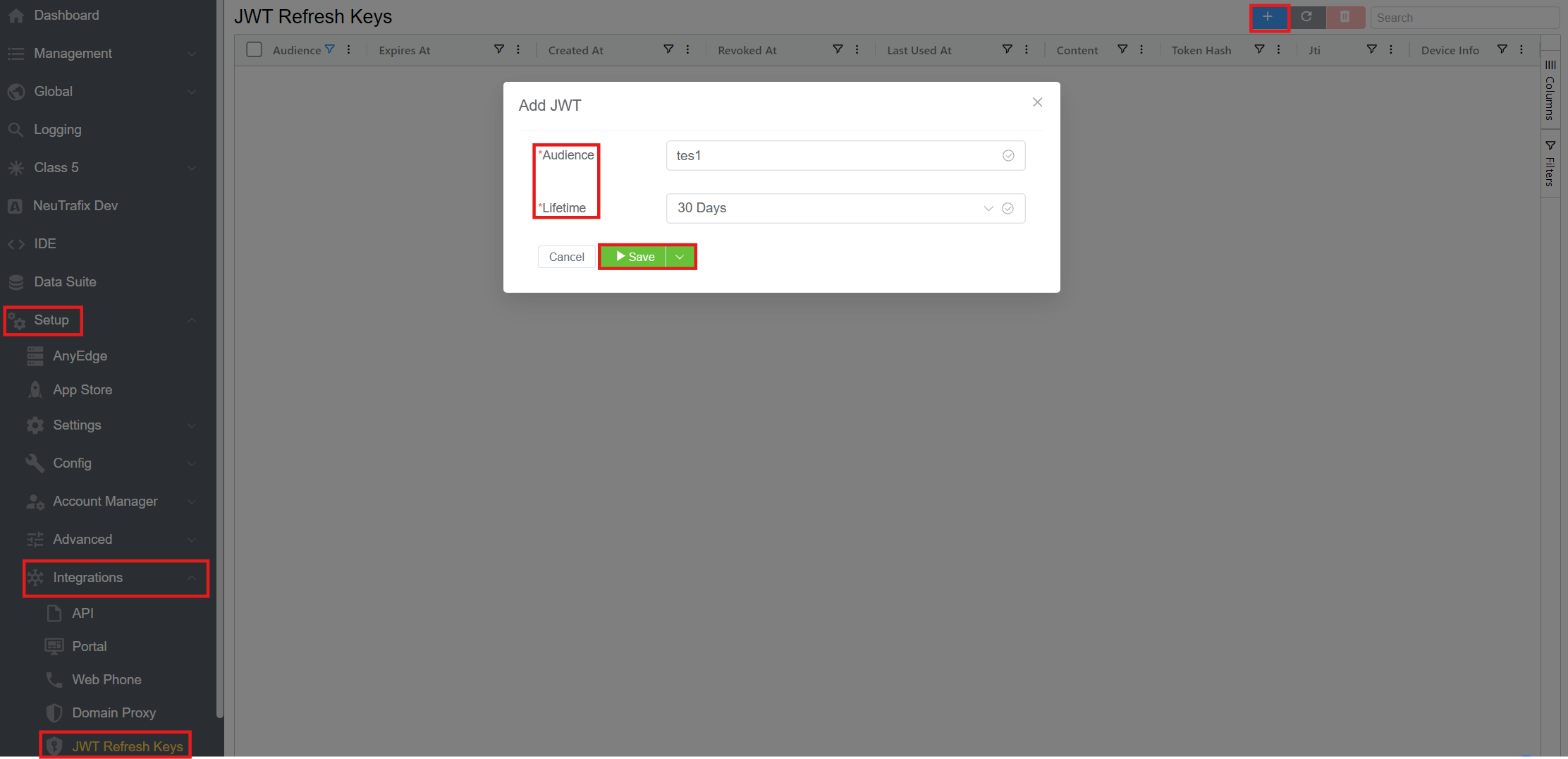
- Click on the blue
+button. Fill in the following fields:- Audience: Specifies the intended recipient of the token, ensuring it is used only by the designated service/application/API.
- Lifetime: Specifies how long the token will remain active before it expires.
- Click
Save.
- Other fields:
- Expires At: Sets the expiration date and time of the token, after which it will no longer be valid.
- Created At: Shows the timestamp when the refresh token was issued, helping track the token’s lifespan.
- Revoked At: Records the time when the token was invalidated, meaning it can no longer be used.
- Last Used: Indicates the most recent time the token was used for authentication or action, helping track token activity.
- Content field: It contains the payload of the JWT, which includes user data or claims (e.g., email: "[email protected]") embedded in the token.
- Token Hash: A unique identifier for the JWT, helping track and manage tokens securely.
- JTI (JWT ID): Its a unique identifier for each JWT, ensuring that each token is distinguishable and can be tracked or revoked individually.
- Device Info: Stores details about the device used for token authentication. For example browser, OS, or device ID, aiding security and auditing.