Cascader¶
Description¶
A Cascader, also known as a Cascade Select or Dependent Drop-down, is a type of input field in a page builder that allows users to select options dynamically based on their previous selections in other fields.
It enables users to navigate through a hierarchical structure of options, narrowing down their choices as they progress through the page.
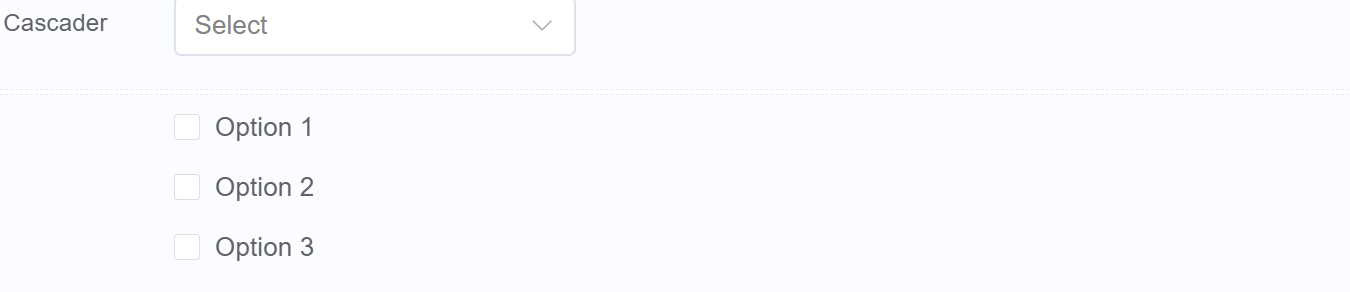
Use Case¶
-
Location Selection Forms: Cascaders can be used to collect location information in a structured manner, ensuring that the selected options are compatible and reducing the risk of invalid entries.
-
Product Configuration Forms: Cascaders are ideal for product configuration forms, allowing users to narrow down their choices step by step and get the exact product configuration they need.
-
Category-based Search Forms: Cascaders can be used to refine search queries by enabling users to navigate through a hierarchy of categories, making it easier to find specific products or items.
-
Organization-based Forms: Cascaders can be used to collect organizational information, ensuring that the selected options are consistent and accurate and making it easier to identify the appropriate person or group to contact.
-
Scheduling Forms: Cascaders can be used to schedule appointments or events by allowing users to select available time slots based on the selected criteria, streamlining the scheduling process and reducing conflicts.
-
Multi-level Address Forms: Cascaders can be used to collect detailed address information in a structured manner, ensuring that the address information is complete and accurate.
-
Hierarchical Classification Forms: Cascaders can be used to classify items or data into a hierarchical structure, making it easier to organize and manage information.
-
Dynamic Form Generation: Cascaders can be dynamically generated based on user input, enabling forms to adapt to specific scenarios and collect relevant information.
-
Data Validation and Error Prevention: Cascaders can be used to enforce data integrity and prevent invalid selections, helping users avoid errors and ensure that the selected data is consistent and accurate.
-
Accessibility Enhancements: Cascaders can improve form accessibility for users with visual impairments or limited motor skills, making it easier for them to navigate through options and make informed choices.
Interactivity¶
Integrating interactivity with cascaders in a page builder involves scripting languages to control the cascader's behavior and respond to user interactions.
Here's a general approach to integrating interactivity:
-
Identify interactive scenarios: Determine the specific scenarios where interactivity should be implemented, such as updating options based on selections, providing real-time feedback, or triggering form actions.
-
Attach event listeners: Attach event listeners to the cascader components to capture user interactions. Common events include 'change', 'select', and 'blur'.
-
Implement event handlers: Write event handler functions that respond to the captured events. These functions should perform the desired interactive behavior, such as updating options, displaying feedback, or triggering actions.
-
Utilize data sources: Access and manipulate data sources, such as external APIs or local data structures, to provide dynamic content and context-aware interactions.
-
Update cascader options: Dynamically update the cascader's options based on user interactions or data retrieval. Use methods like loadOptions() or enableOption() to modify the options.
-
Provide real-time feedback: Display visual or textual feedback to users based on their selections. Use methods like highlightOption() or displayMessage() to provide feedback.
-
Trigger form actions: Trigger specific form actions based on user interactions in the cascader. Use methods like submitForm() or showAdditionalFields() to perform actions.
-
Handle errors and exceptions: Implement error handling mechanisms to gracefully handle invalid selections or unexpected input. Use try-catch blocks to catch and handle errors.
-
Test and refine: Thoroughly test the interactive cascaders to ensure smooth functionality and user-friendly interactions. Gather user feedback and refine the implementation accordingly.
Examples may include:
-
A product configuration form could use interactivity to dynamically update the available variants and pricing based on the selected product model and other options.
-
A location selection form could use interactivity to provide real-time feedback on the validity of the selected address and suggest alternative options if necessary.
-
A scheduling form could use interactivity to highlight available time slots based on the selected date, service provider, and other criteria.
-
A multi-level categorization form could use interactivity to reveal additional subcategories or filters based on the user's previous selections, refining the categorization process.
-
A dynamic form generation tool could use interactivity to dynamically generate new cascader options or form fields based on the user's input and choices.
API¶
Events¶
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
onChange (element) |
The onChange event occurs when the value of a field is changed |
onFocus (element) |
The onfocus event occurs when a field gets focus |
onBlur (element) |
The onblur event occurs when a field loses focus |
Methods¶
| Name | Description | Parameters |
|---|---|---|
this.addClassName |
Add style class to a form item | (fields: String|String[], className: String) |
this.removeClassName |
Remove style class from a form item | (fields: String|String[], className: String) |
this.getComponent |
Returns a component whose id has been passed as a parameter | (component_ID: String) : Object |
this.getValues |
Gets the current values of all fields | () : Object |
this.hide |
Hides the field | (fields: String|String[]) |
this.show |
Displays the field | (fields: String|String[]) |
this.disable |
Disable cascader from user interaction | (fields: String|String[]) |
this.enable |
Enable cascader from user interaction | (fields: String|String[]) |
this.refreshFieldDataSource |
Refresh the datasource data bound to the whole page | |
this.setData |
Set the data in the field. The Value object should be of type { componentId: componentValue } | (Value: Object) |
Info
- The show() and hide() methods can also be used to control the visibility of the cascader in response to user input.
- Fields refers to a component ID or a list of component IDs. You can fetch the ID from the Component Attribute panel in the Page Builder.
- Before using this.show(fields), make sure the component is hidden. This can be done using this.hide(fields) or by enabling the Hidden checkbox in the Component Attribute panel.
- Before using this.enable(fields), make sure the component is disabled. This can be done using this.disable(fields) or by enabling the Disabled checkbox in the Component Attribute panel.
Steps to use the methods for the Page Builder components¶
- Go to Form Attribute Action Panel Setting (Mounted | refresh | click 'Add action').
- Write the method/code as shown in the Example below.
- Click on
Save. - On the main screen click on
Saveagain. - Click on
Previewto see the code in action.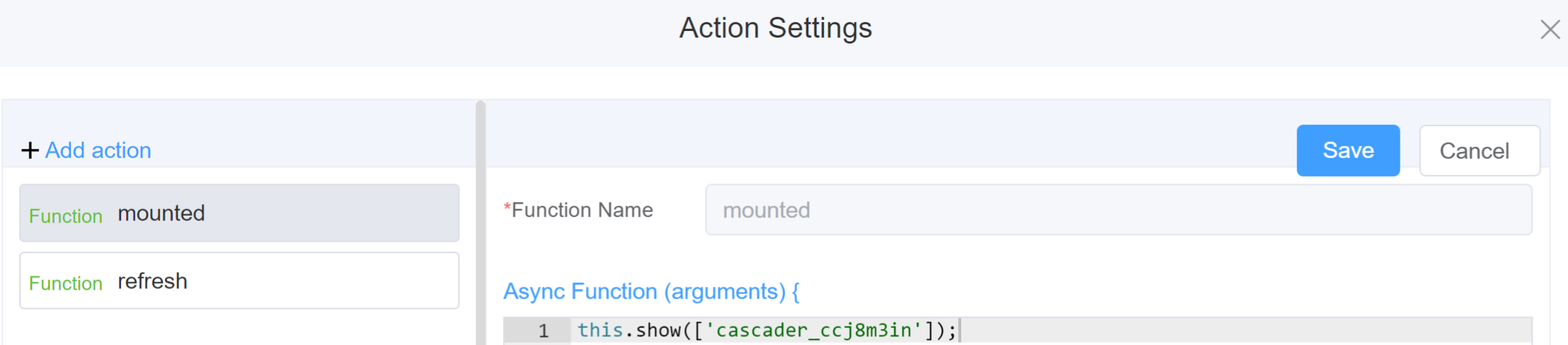
Example
-
this.addClassName(fields, className)- Go to Form Attribute Style Sheets add the class
.abc{ // abc is the class name background-color: red; } - Follow the steps mentioned above, under Steps to use the methods for the Page Builder components
this.addClassName('cascader_ccj8m3in', 'abc')
- Go to Form Attribute Style Sheets add the class
-
this.removeClassName(fields, className)this.removeClassName('cascader_ccj8m3in', 'abc') -
this.getValues(fieldName)var data = this.getValues(); console.log(data); -
this.hide(fields)var fields= ['cascader_ccj8m3in'] this.hide(fields) -
this.show(fields)var fields= ['cascader_ccj8m3in'] this.show(fields) -
this.disable(['fields'])this.disable(['cascader_ccj8m3in']) -
this.enable(['fields'])this.enable(['cascader_ccj8m3in']) -
this.getComponent('component_ID')var cascadername = this.getComponent('cascader_ccj8m3in'); console.log('getComponent', cascadername); -
this.setData(Value)this.setData( { "cascader_oe6xkjqr": [ "Option 1", "Option 1 - children" ] } ) -
this.refreshFieldDataSourcemake the function or data as dynamic
Config¶
| Name | Description | Icon |
|---|---|---|
| ID | The cascader component's unique identifier | 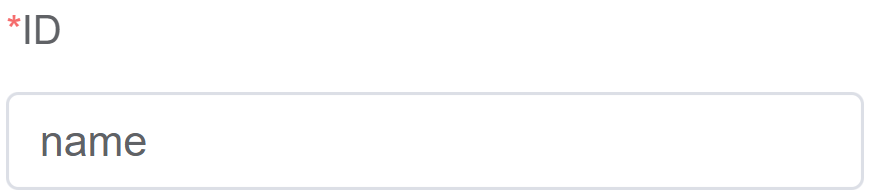 |
| Name | [Optional] The display name of the cascader |  |
| Width | [Optional] The width of the field | 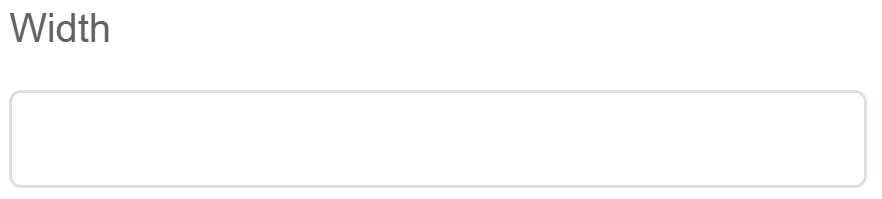 |
| Label Width | Width of the label associated with an input field. It determines the horizontal space occupied by the label text | 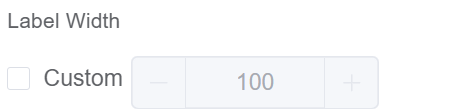 |
| Label Wrap | If the label is longer than the allowed width the text will continue on another line |  |
| Hide Label | Hides the label on the page |  |
| Placeholder | The short hint is displayed in the input field before the user enters a value | 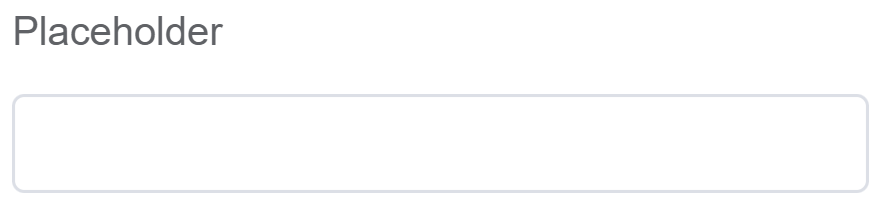 |
| Text Prompt | A description to aid the user when completing the field |  |
| Multiple | Enable this option if you want your users to select multiple options from the cascader's list of choices |  |
| Searchable | This method makes it easier for users to find and select options in forms with many choices, especially when they're organized hierarchically |  |
| Optional any node | Allow users to pick any node in the hierarchy, even if it's unrelated to their previous choices, offering flexibility in option selection |  |
| Option | Choose either Static or Dynamic way of adding data to the oprions of the Cascader Static data refers to a fixed set of options that are predefined and loaded into the cascader at the time of initialization Dynamic data are options fetched as needed from sources like databases or APIs. The cascader updates choices based on user selections. You select from Data source which refers to the origin of the data; Function which refers to the code that manipulates the data, and Assigned Value which refers to the specific value stored or associated with a data element |
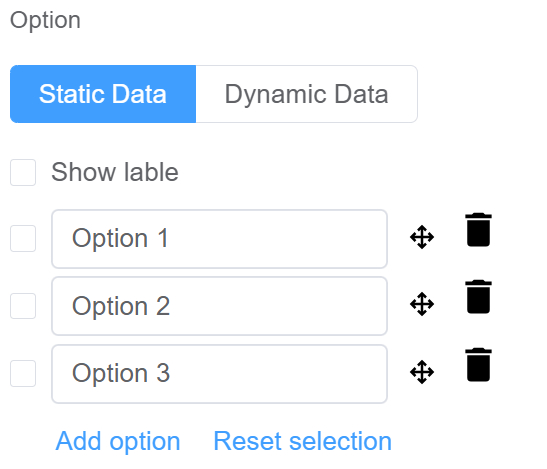 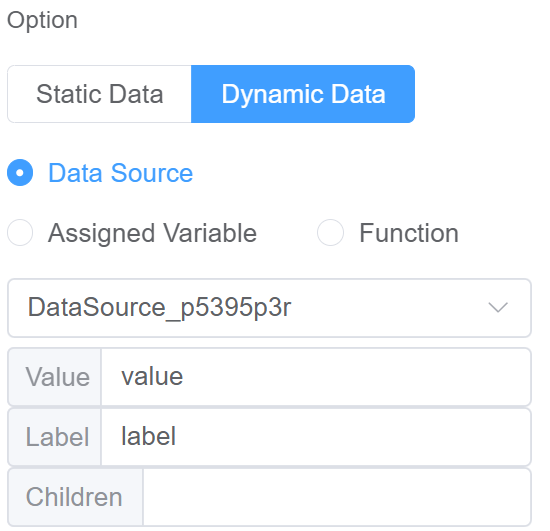 |
| Default Value | It specifies the initial option that's selected when the form is loaded |  |
| Custom Class | An HTML class attribute which allows further customisation See Form Attribute > Style Sheets |  |
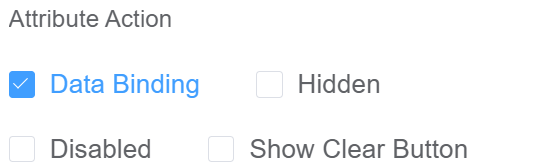
| Attribute Action | Enable Data Binding to connect the data to UI Enable Hidden action to hide the field Enable Disabled action to make the field unusable Enable Show Clear button action to make the clear button visible. |
 |
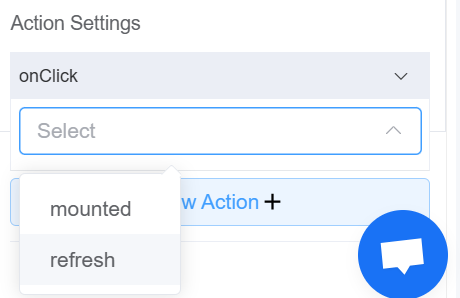
| Action Settings | Click on the drop-down to select the pre-defined methods you wish to apply to your component. In this case, you can choose either mounted or refresh for onChange, onFocus, or onBlur |
 |
Validation¶
Form validation is the process of checking the data entered into a form to ensure that it's valid and complete.
This helps to prevent users from submitting forms with invalid data, which can cause problems for the application that's processing the form.
Form validation can be performed using a variety of methods, including:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Required | If enabled, then the field value can't be empty, otherwise an error message is emitted |
| Custom Validation Rules | (rule, value, callback) => { |
| rule: Verification rule, you can view the verification configuration information through this parameter; rule.field can get the field identifier of the current verification. | |
| value: Value of the current field | |
| callback: Callback function (must be called) upon completion of validation; callback('Error message')/ callback(new Error('Error message')). These are two ways to return an error message. |

Info
- The callback() function is also called to verify success in the custom validation method.
First time User?¶
If you are using the Page Builder components on the ConnexCS platform for the first time, we request you to use our guide on steps to use the Components.