Ingress Routing¶
Management Customer [Customer Name] Routing
Overview¶
Ingress Routing is the process that allocates an incoming call (dialed by our customers) based on the assigned Customer Rate Card, which then Egresses the call to a specified provider. This makes it possible to deploy several rate cards both with and without a prefix.
Ingress Routing Process¶
- Traffic Entry: Incoming call traffic enters ConnexCS
- Authentication Check:
- The system verifies the call (outbound) based on the defined authentication method.
- If authentication fails, the call is rejected.
- Routing Decision:
- Calls are routed based on predefined rules,Tech Prefix or Dial Strings.
- Call Processing:
- Successfully authenticated calls proceed to the designated destination.
- Billing and reporting data are updated accordingly.
How it works?
graph TD
A[Traffic Entry] --> B[Authentication Check]
B -- Authentication Passed --> C[Routing Decision]
B -- Authentication Failed --> D[Call Rejected]
C -- Apply Routing Rules --> E[Call Processing]
E -- Forward Call --> F[Provider]
E -- Update --> G[Billing & Reporting]The multiple routes can be differentiated on the basis of Tech Prefix or Dial Strings.
Routing Templates and more
Create templates for customer routing in Routing Global.
For more information on Routing, see Routing Setup in our Video Guides for a detailed walk-through.
You can find additional documentation in the Routing Overview and Routing Strategy sections.
Configure Routing¶
View and configure existing routes on the Routing tab in the Customer card. To create a new route, click + in Ingress Routing.
Basic¶
-
Rate Card: Also known as Tariff, this allows you to select the rate card used on a customer's account. You can handle these calls in the following three ways:
- Internal: Send a call to the ConnexCS Class5 (Voice Mail, Interactive Voice Response (IVR), etc.). If selected, the "Auto" option becomes available, which will generate dial strings from all possible internal extensions.
- Extension: (uses SIP users in Customer Auth configured SIP Users) Send a call to a Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) Authenticated user on the account.
- Customer IP: (uses IPs in Customer Authconfigured IPs) Send a call from an agent back to the customer's Private Branch eXchange (PBX), using either the Tech Prefix (e.g.: #9) or a Dial String (e.g.:
^[0-9](4)$).
-
Tech Prefix: This lets you distinguish a route from an inbound party. When several customers share the same IP address, each customer needs an individual Tech Prefix so the switch can route calls correctly. It enables service providers to differentiate between several rate cards.
- Dial String Prefix Set: Helpful for commonly used sets of prefixes. Rather than entering a complete list of prefixes for the UK, for example, you can create a predefined Prefix Set (defined under Setup Advanced Prefix Set) and then select it here for appropriate customers.
-
Dial String: Only allows a dialled number to pass through if it matches the defined dial string (or "dial pattern"). (If you customer enters nothing, it matches everything and attempts to send all calls).
-
Enabled: You can enable and disable the routes here.
Price Limits¶
-
Capped Rate and Provider Capped Rate: Set the maximum cost of a call. Calls that exceed the set rate won't get connected. For example, for customers with flat rate accounts, which allows to dial all UK numbers but premium numbers, you would set the Provider Capped Rate at 0.01, so any call that the provider might charge over that amount wouldn't get completed.
-
Profit Assurance: When
Enabled, only calls that are profitable pass-through; any call that costs more than the retail rate aren't allowed to complete. This is particularly useful for A-Z routes or NPA-NXX rate cards.
When Profit Assurance Fails to Operate
A. Profit Assurance may appear to fail, often due to:
1.Incorrect Billing Configurations:
Billing increments (e.g., 6/6, 30/6, or 60/60) play a significant role in profitability. A mismatch between the billing increments of your carrier and customer rates can lead to unexpected losses.
For example: If you buy at 30/6 and sell at 6/6, you lose money on shorter-duration calls because of rounding discrepancies.
2.Profit Assurance Enabled but Losses Persist:
Even with Profit Assurance enabled, losses may occur due to:
- Specific call durations where rounding favors the carrier.
3.Misunderstanding Call Connection Logic:
Profit Assurance does not retroactively check call profitability during ongoing calls. If the buy rate is temporarily higher than the sell rate due to duration or rounding, calls may still connect.
-
Block Connect Cost: Block any call that has a connection fee.
-
FTC DNC Report ANI Block (USA): When
Enabled, ConnexCS will take a copy of FTC data (using the FCC's Do Not Call (DNC) Reported Calls Data API) and add it to the system. We can then block callers from known spammer CLI / ANI's. -
DNO: Click here to know more about it.
-
Stir Shaken Min Attest: It enables the selection of STIR/SHAKEN attestation levels for validating incoming calls. Users can configure the system to permit only calls that meet specific attestation standards. The available validation levels are as follows:
- A: Permits only calls with attestation level A, the highest level of trust. Calls with attestation levels B or C will be blocked.
- A + B: Restricts incoming calls to only those with attestation levels A or B. Calls with attestation level C will be blocked.
- A + B + C: Allows calls with any attestation level (A, B, or C) to pass through.
Note
In all cases, calls without attestation will also be blocked.
Capacity Limits¶
-
Channels: Set the maximum number of channels/live calls allowed for this route.
-
Max Duration: Set the maximum amount of time (in seconds) that the call gets to exist before getting terminated, typically for the case of a missed
BYE.
Call Timeouts
A VoIP call is stateful, even though its protocol is stateless. This means that both the sides should be informed on finishing of the call. They do this with a BYE message. If the BYE message goes missing, the call will continue forever.
Max Duration is a method for setting up Missing BYE Protection. Another approach is to use a SIP Ping to determine when the connection has timed out. This sends a SIP packet to the remote end of the conversation every 30 seconds. This checks to see if the other side is still aware of an ongoing conversation. If it does'nt receive a response or informed that the conversation is not active, it disconnects the call.
RTP Time-out: This is another way to check for an active call based on whether audio is passing. If there is no audio passing for a pre-set interval, our Real-time Transport Protocol (RTP) array will notify the switch and instruct it to end the call. This won't work if RTP Mode is set to direct.
Asterisk pings
Asterisk doesn't have SIP Ping (OPTIONS) enabled by default. If your customer / carrier is using Asterisk, you may need to disable this if they don't have it enabled on their side, as calls will typically disconnect after 30 seconds.
-
Flow Speed (CPS): Limits the calls per second. You should set this for each customer card assigned to the customer account.
-
CPS Spike Buffer: Limit a spike of calls by spreading them over a longer period of time. This essentially manages a large volume of calls over a short period of time. Once the buffer limit reaches its threshold, the calls per second kicks in, distributing the spike of calls.
-
ASR Plus assists capacity management by helping you define how to handle connections for known failed numbers. For information on the ASR Plus options, see ASR Plus Details below.
-
Balance Disconnect this feature checks the balance every 60 seconds. It will disconnect the call when the balance plus the debit limit is below $0.
Note
Balance Disconnect only takes into account the completed calls; it excludes any active calls.
ScriptForge¶
- ScriptForge: Set a custom JavaScript to run from within the ConnexCS platform in-line with the call. Some example operations could be checking a Do Not Call list or forcing a CLI. It allows running JavaScript scripts inline with call processing, enabling real-time modifications and checks.
For more information about setup and operation, see the ScriptForge page.
Key Features and Benefits¶
- Custom Call Handling: Modify CLI, check block lists, enforce specific caller IDs, or track call frequencies.
- Integration with Data Storage: Uses TOML for configuration and variable storage.
- Carrier-Level Routing Controls: Includes include (whitelist) and exclude (blacklist) carrier options.
- Timeout Settings: Defines the duration a script is allowed to run before termination.
- Timeout: Set how long the script may run.
- Timeout Action: This option lets you decide the action when the timeout occurs.
- VARS (TOML): Select the variables you want pass into the ScriptForge script.
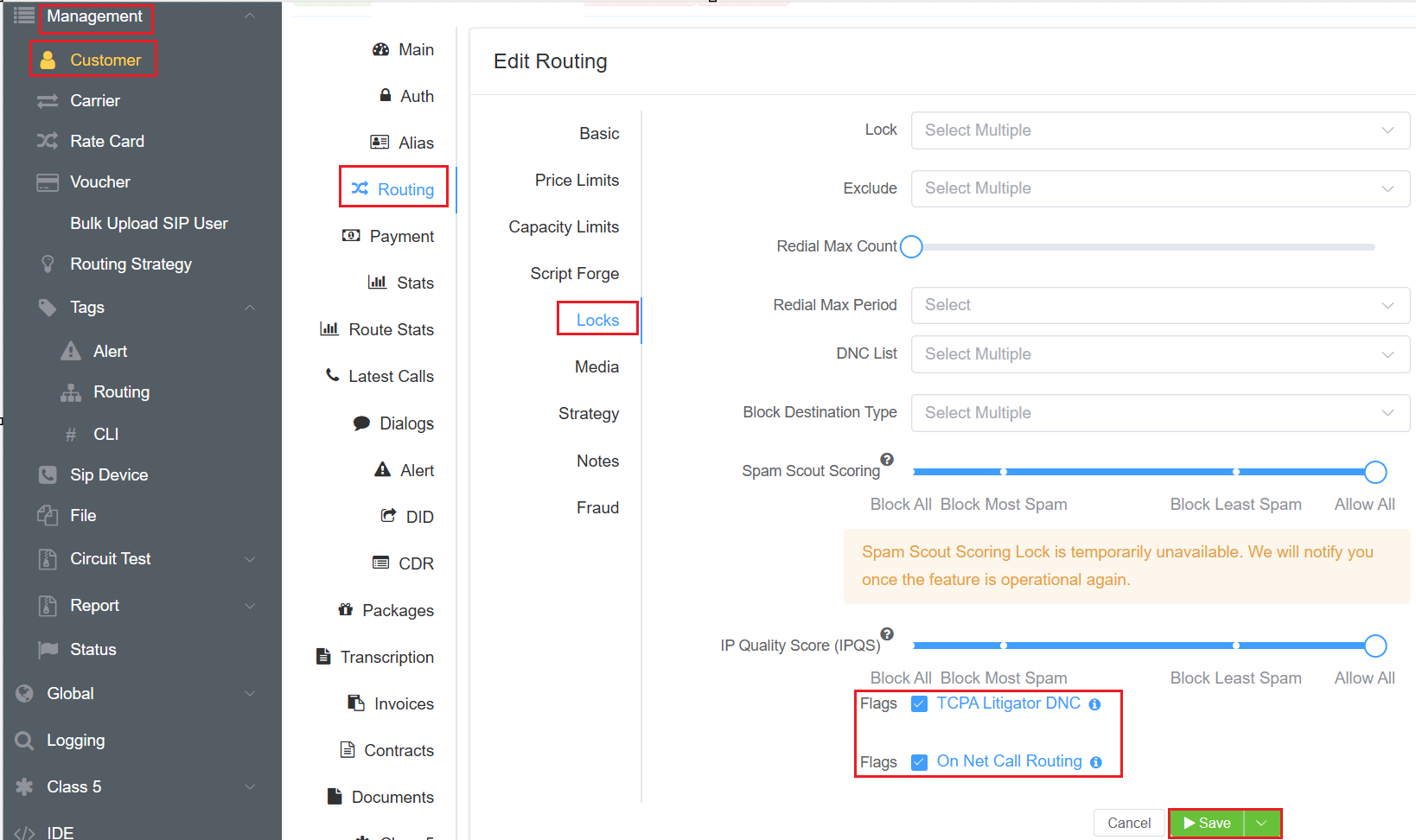
Locks¶
- Lock (Allow): Ensures calls are only routed through specified carriers.
- Exclude (Deny): Exclude access to one or more rate cards in the list of available providers.
- Redial Max Count: This a smart limitation feature that allows the carrier to restrict the maximum number of times their customers can redial. After reaching this limit, customers must wait for a certain amount of time defined by the Redial Max Period. For example, you select 5 for this field, it means your customer can dial only 5 times.
- Redial Max Period: It refers to the duration of time during which a customer is restricted from making further redial attempts to the same number after reaching the maximum redial count.
-
DNC (Do Not Call) List: The customer won't be able to able to dial the numbers in the specified DNC list. You can add the list of numbers in the Database.
Apart from your own DNC list you can also choose United States Federal DNC. Choosing not to accept telemarketing calls is possible because of the National Do Not Call Registry.
-
Block Destination Type: You can select and block the calls to various destinations (carriers) like Mobile, Fixed, Paging, etc.
-
Spam Scout Scoring: It blocks Spam calls based on the CLIs. You can either Block All, Allow All, Block Most Spam, or Block Least Spam.
Exclude Use Case
If a customer reports an issue with a carrier or route, you can come here and set the carrier / route to Exclude and Save, then come back and remove it, and do a Delay and Save for a later date.
Example: Redial Max Count and Redial Max Period
For example, if you have set Redial Max Count (maximum redials in a given time period) as 4 and Redial Max Period as 24 hours for your customer, then your customer can resume redialling after 24 hours after the last call "starts"/last call was placed. For instance, 4 Redials in 24 hours (Time starts from 9:00 AM)
| Redial number | Time |
|---|---|
| Redial number 1 | 10:00 AM |
| Redial number 2 | 01:00 PM |
| Redial number 3 | 04:00 PM |
| Redial number 4 | 08:00 PM |
The last(4th call) redial call was placed at 08:00 PM, so the customer can start redialing at 08:00 PM the next day.
IP Quality Score (IPQS): It blocks spam calls based on CLIs. It won't allow the CLIs of having a specific spam score that you've selected to pass through the system. For more information on IPQS, click here.
Warning
The IPQS feature requires a paid subscription. To enable this feature navigate to Setup Settings Account and enable this feature.
Check Pricing here for a single lookup.
You can set a Max Daily Quantity for your customer's lookups. This restricts them to using only the specific number you allocate, ensuring controlled usage.
We don't charge you again if you repeat your lookup within 24-hours of time-span.
Flags:
-
TCPA Litigator DNC: Enabling this flag blocks outbound calls to known TCPA Litigators.
-
On Net Call Routing: Enabling this flag determines if a call should be routed internally between customers to DID's.
Call Routing Process
graph LR
A[Customer A makes a call using the route with the ON NET CALLING flag] --> B{Syatem checks the dialed number and compares it against DIDs added to the account across all customers}
B -- Yes: If the dialed number matches any DID in the account--> C{Route call internally to the matching DID}
B -- No: If the dialed number doesnt match any DID in the account--> D{Route call externally via carrier as configured}Media¶
Transcoding: Transcoding manages different audio codecs to ensure compatibility between the calling and receiving systems.
Enter the number of channels allowed for transcoding. This is a limited option. The best use case is for customers in low-bandwidth areas that want to use G.729.
Be aware that if you don't have enough transcoding capacity, calls will fail.
-
SIP Ping: To SIP Ping protects from long duration calls by periodically verifying call connection status. Send regular pings to ensure both sides of a call are still up.
Enabledis the recommended setting. -
Benefits:
- Prevents ghost calls.
- Ensures real-time call session awareness.
| Option | Result |
|---|---|
| Disabled | No SIP pings will be sent |
| Enabled Both Sides | SIP pings sent in both directions |
| Enabled (Downstream Only) | SIP Pings sent to the location where the call originated |
| Enabled (Upstream Only) | SIP Pings sent towards where the call is TO (terminated) |
- SIP Session Timer (SST): SST is Passive by Default, but Enabled is the recommended setting. When enabled, SST ensures there is no ghost or long-duration calls get billed when one or both sides have hung up. A timer activates when the call starts and refreshes the call every X number of seconds by sending a RE-INVITE. SST has surpassed SIP Ping Timeout as the best way to prevent long-duration calls. Note that any SST shorter than sixty (60) seconds gets rejected.
Session Timers periodically revalidate call sessions to ensure continued connectivity.
| SST Option | Result |
|---|---|
| Default | Passive SST, No headers gets changed and no SST gets engaged, all RE-INVITES will propagate through the system enables |
| Enabled Both | ConnexCS will send SIP Session Timers to both legs of the call |
| Enabled (Upstream) | ConnexCS will use SST with the carrier |
| Enabled (Downstream) | ConnexCS will use SST with the customer |
| Suggest | Session-Expire headers and Min-SE gets added to packets sent to the carrier encouraging the use of SST |
| Disabled | All timer headers are removed |
Warning
SIP Ping and SIP Session Timers can't be enabled at the same time.
- RTP Media Proxy: This defaults to Auto, but selecting a zone is the current recommendation. The following options allow you to set where RTP media server for this route for this customer:
Functionality and Benefits
Functionality:
-
Ensures media flows through the most efficient route.
-
Reduces audio latency by keeping media within the same geographical region as the customer and carrier.
Benefits:
- Minimizes delay in audio transmission.
- Enhances call quality by reducing packet loss.
Direct RTP (no proxy)- Bypass ConnexCS, so media flows directly between the customer and carrier. If the customer is using a firewall or other NAT device incorrectly, then media may not flow between the carrier and the customer. Using this setting also means that if there are audio issues, the issue can't be ConnexCS. Since it isn't likely to be the carrier, the issue would typically exist on the customer's end.
Disadvantages & Risks
- Leaks Carrier Information: Direct RTP reveals the carrier’s SDP address.
- Risk of Disintermediation: Customers can bypass ConnexCS and deal with carriers directly.
Best Practice
- Always inform customers about the risks associated with Direct RTP.
- Recommend using RTP Proxy when confidentiality and NAT traversal support are needed.
Zone- Choose any of the regional servers, but it's recommended that you select a location close to a provider or your customer. Temporarily selecting a different region to route media traffic can be helpful in diagnosing call problems.
The recommended RTP Media Proxy servers are the Closest (To ConnexCS) Server or the Closest (Elastic) Server.
- RTP Proxy Mode: Routes media optimally while keeping signaling intact.
Strict- This will enforce the proxy engagement. If the proxy can't engage with the call, the call won't get established. If a selected proxy server fails, the call is dropped.
Free accounts are limited to how many RTP Proxy channels get enabled, this may prevent calls from connecting if you have more channels than our free accounts allow you to have.
Relaxed- This will make the best efforts to engage the RTP Proxy; if it can't get engaged because of either network errors, or because you don't have enough RTP capacity, the calls will connect directly. If the selected proxy server fails, the call is routed directly to the carrier. If a connection via our service fails and you have selected relaxed, it will automatically fail over to the backup.
When should I use RTP Proxy?
Use an RTP Proxy if you don't want your customers to know your providers.
When should I avoid using an RTP Proxy?
You have other equipment in your SIP set-up that will act as a Media Relay or you want to run a test to see if audio problems are related to the ConnexCS switch.
RTP Proxy distinctions
When a call gets established between the customer and the provider, audio can be setup in one of two ways:
| With RTP Proxy | Without RTP Proxy | |
|---|---|---|
| Audio Path | Indirect | Direct |
| Audio Quality | Excellent | Unbeatable |
| Latency | Low | Lowest |
| Information Leakage | No | Yes* |
While it's doubtful that any information will get logged in the customer / providers switch when the audio gets engaged, it's possible for an engineer to learn this information from a SIP trace, PCAP, or by looking at transit locations. DTMF Detection ONLY works when RTP Proxy mode gets enabled.
Private RTP Server
We provide deployment of the Private RTP Server (Media) to our customers, which is liable to some cost. You may be able to add Private RTP Servers to the following fields:
-
Call Recording: This allows you to record and store calls, which are then found in:
- Logging
- Management Customer [Customer Name] CDR
- Management File Recording
Additional Charge
An extra charge per recorded call gets added to existing fees or charges, so choose carefully how many calls to record. Check Pricing here.
Disabled- no calls get recorded.
Sampling- Choose from a 1%, 5%, 25%, or 50% sample of your calls (e.g: 1% will record 1 of every 100 calls, 25% will record 25 of every 100 calls, etc.).
Enabled (Always On)- Record all calls.
The Call Recording setting is disabled
You need to enable the feature first on the account in Setup Settings Packages before it gets enabled here for individual customers.
- Block DTMF: This option allows you to either
passorblockDTMF through your calls.
Make sure your carrier supports the DTMF feature.
-
Flags (Active RTCP Generation): Enabling this feature generates RTCP packets, while disabling it allows them to pass through undisturbed.
-
RTP Codec: This fields allows you to have more specific control over the Codecs you choose for your system. After the selection you can assign various Permissions to the Codecs you select.
-
Types of Permissions include:
- Except: This permission allows you to block all the codecs apart from the ones in the Whitelist. Codecs that weren't included in the carrier's initial codec list won't be taken into consideration.
- Offer: Offer also blocks the codecs apart from the ones in the whitelist and provides flexibility to change the order of the codecs in the list as well. Thus, the first codec in the list is treated as the primary codec (at the output) even if it was the last codec in the list.
- Consume: Identical to mask but enables the transcoding engine even if no other transcoding related options are given.
- Transcode: Allows the addition of codecs in the offered codec list even if the codecs weren't included in the original list of codecs. Here, transcoding engine will be engaged meaning behind-the-scenes translation process is happening to ensure communication.
You can only add those codecs which are supported by your device for both encoding and decoding process.
One limitation of using this option is that it will strip-off all the unsupported codecs. Note that using this option doesn't necessarily always engage the transcoding engine. If all codecs given in the transcode list were present in the original list of offered codecs, then no transcoding will be done.
When you use this permission it enables you to mark/modify the Ptime. - Strip: This permission allows you to remove the selected codecs or RTP Payload types from the SDP. Codecs removed using this option behaves as if they never existed in the SDP.
Strip Transcode Explanation G729A Opus G729A is unavailable for transcoding - Mask: This option allows you to filter-out the selected codec from the output. Mask works well in combination with Transcode option. For example,
Input/Offering side Mask Transcode Output/Outgoing Offer Explanation G729A G729A Opus Opus Transcoding happens between G729A and Opus but output is Opus, G729A is filtered out from outgoing offer G729A Opus G729A and Opus Transcoding happens between G729A and Opus but outputs are both Opus and G729A since G729A wasn't filtered out - Accept: This option is similar to Strip and Mask but it isn't removed from the codecs offered list. When you select this option, the selected codec is offered to the remote peer (output/outgoing offer), if the remote peer rejects the offered (incoming) codec it will be used for transcoding and is accepted by the input/offering side. In short, Accept permission allows your device to use codecs offered by the remote peer even if they weren't your initial choice.
Input/Offering side Accept Transcode Output/Outgoing Offer Explanation G729A G729A Opus Reject Transcoding still happens between G729A and Opus -
Ptime(ms): This value determines the length of time each box (RTP packet) can hold. A higher ptime means each packet carries a longer chunk of audio/video data (bigger box), while a lower ptime means shorter chunks (smaller boxes).
-
Strategy¶
For advanced routing, click to select a Prefix Set and assign a Routing Strategy. This gives you greater control over how routes get selected for a given customer.
Notes¶
- Public Notes: Notes entered here get displayed on the Customer Portal when logged in.
- Private Notes: These will get displayed to the customer in the Control Panel.
Fraud¶
- Fraud Profile: Apply one of the Fraud Profiles configured under Setup Advanced Fraud Profile.
-
Fraud Mode: Specify how the profile will gets into application, this is dependent on the Fraud Mode Thresholds configured in the Profile.
DisabledLow - Alert or Block CallsHigh - Block Calls or Account
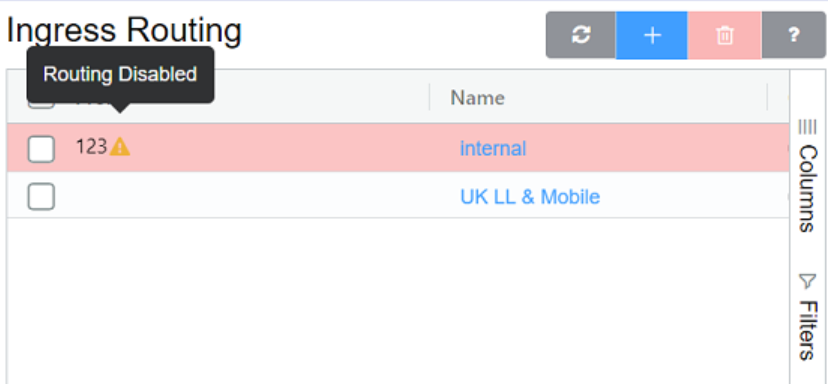
Disabled Routes¶
Routes highlighted in red on the customer Routing page gets disabled. Open the route, click Enabled, and then Save to enable them
Tech Prefix¶
1. What is Tech Prefix?
A Tech Prefix is a string of numbers, added to the dialed number (DNIS) before sending the call.
2. Purpose of Tech Prefix:
- Customer Identification: It allows routing calls for different customers using the same inbound IP by specifying which customer the call belongs to.
- Routing Control: It can be used to direct calls to specific routes or carriers depending on the prefix.
3. How it Works?
graph LR
A[Tech prefix added to the dialed number before sending the call] --> B{VoIP identifies the Tech Prefix}
B --> C{Strip Tech Prefix}
C --> D{Route Call Based on Rules configured for that Prefix}Example Workflow
flowchart TB
A[Call Ingress] -- A call is made to a number with a tech prefix (e.g., 123*123456789) ---B[Prefix Matching] -- The system checks if the prefix 123* matches a configured customer or route ---C[Stripping Prefix] -- The system strips off the 123*, leaving the actual number 123456789.---D[Call Routing] --Based on the tech prefix, the call is routed to the associated customer or carrier ---End4. Advantages
- Flexibility in routing calls to different customers using a shared IP or trunk.
Example
graph
A[Incoming Call with 001*123456789] -- Call will be routed to Customer A --- B[Customer A Prefix: 001]
subgraph Customers
B[Customer A Prefix: 001] & C[Customer B Prefix: 002]
end
B[Customer A Prefix: 001]-- Prefix 001* will be stripped before passing the call to the destination number 123456789 --- DestinationAnswer Seizure Ratio Plus Details¶
ASR (Answer Seizure Ratio) is the number of connected calls divided by the total number of calls (represented as a %).
ASR Plus is a proprietary ConnexCS technology that filters known failed, non-existent / working numbers between the customer and the terminating, or destination, carrier.
It's useful with larger call volumes.
Unless it's turned off or customized otherwise, ASR+ is active for 90% of calls, which grants the opportunity for the database replenishment.
It enhances call routing by tracking the validity of dialed numbers over a 30-day period. It improves efficiency by blocking known invalid numbers and allowing successful calls to proceed.
Key Features¶
- Call History Tracking: The system remembers if a number was successfully connected or failed in the last 30 days
-
Automated Call Blocking:
- If a number failed previously with a 404 error, it is automatically blocked for future attempts.
- If a number has never been seen, it is allowed through.
- If a number is connected successfully, it continues to be allowed.
-
Customizable Configurations: Users can tweak settings to define how ASR+ handles call failures and successes.
- Carrier Load Optimization: Reduces unnecessary call attempts, preventing high call-per-second rates to invalid numbers.
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| Off | ASR+ Disabled |
| ASR+ (Low) | Active on 30% of calls |
| ASR+ | Active |
| ASR? | When ASR+ gets enabled on the provider card |
| ASR+? | When ASR+ gets enabled on the provider card, only known connected calls pass-through specific providers |
| ASR++ | Only known connected calls pass-through (not used frequently because it's typically overly strict) |
Advantages of ASR
- Prevents excessive failed call attempts from impacting service quality.
- Reduces response time for your customers.
- Improves the ASR of the traffic that your upstream carrier sees.
- Highly effective for call centre traffic.
- Enhances call completion rates.
- Reduces wasted carrier resources and associated costs.
Disadvantages of ASR
- Marginal impact on your NER due to false positive matches. This is usually kept within tolerances of < 0.1%.
- Doesn't offer improvements for all destinations.
Strategic Routing¶
Strategic Routing feature allows creating a Routing Strategy that, when applied, will route calls to specific provider rate cards, completely bypassing any routing configured in the customer rate card.
Steps for implementation¶
-
Create a Routing Strategy:
-
Navigate to Management Routing Strategy blue
+icon . - A window will pop-up to create a new strategy.
- Fill in the following details:
- Name of the strategy
- Select the Strategy from the drop-down menu.
- Enable the Override Routing option.
- Select a Rate Card from the drop-down menu.
- Click
Save.

2.Apply the Strategy to a Customer:
- Navigate to Management Customer [Customer Name] Routing Ingress Routing blue
+icon Strategy blue+icon. - Select the Prefix Set or enter the Prefix.
- Select the newly created Routing Strategy for the customer.
- Click
Save.
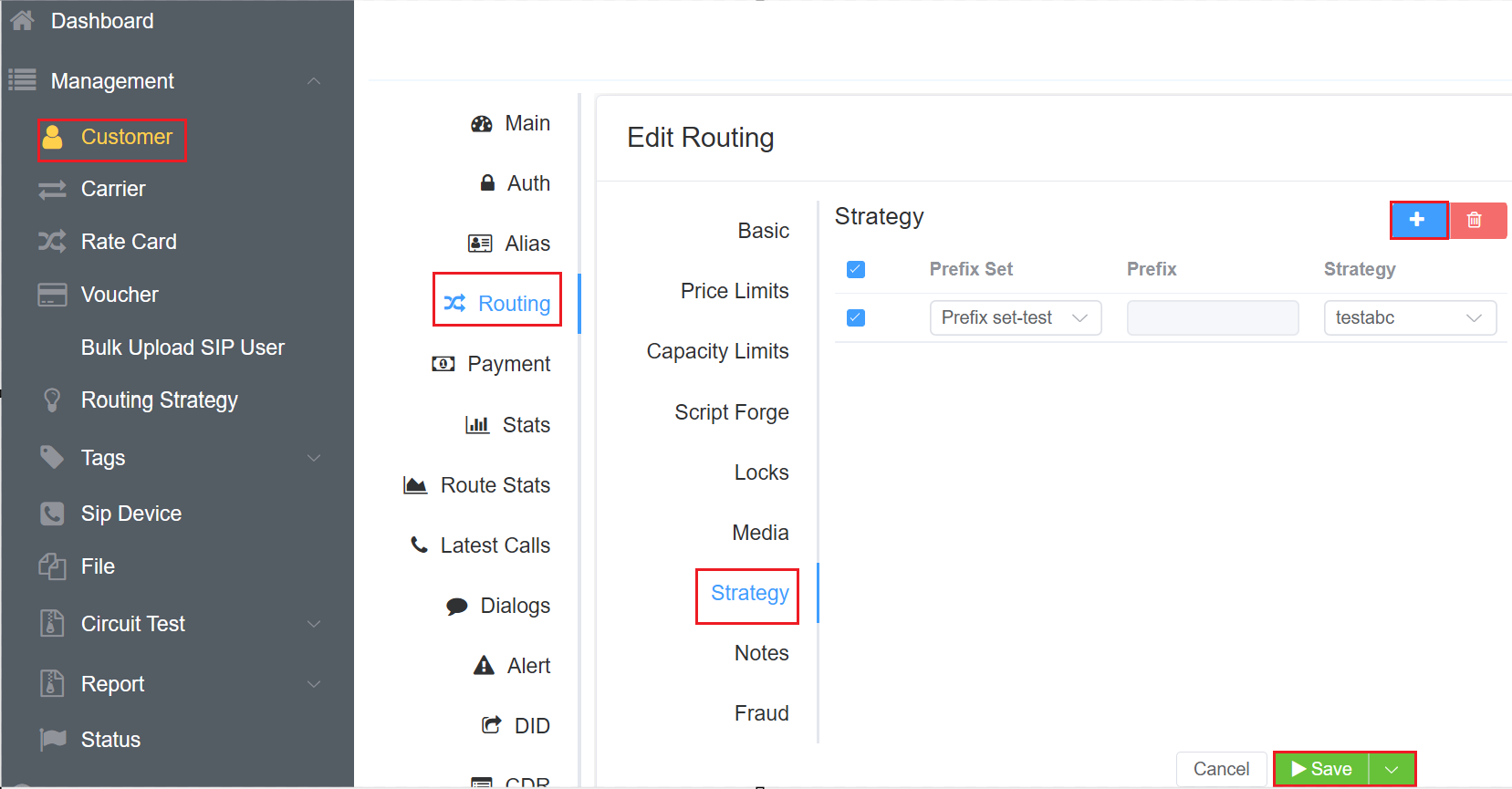
Routing Behaviour
Once applied, calls from the customer will now route based on the provider rate cards specified in the strategy. Important: This will completely ignore the routing set up in the customer rate card.