Auth¶
Management Customer [Customer Name] Auth
Use the Auth tab to configure IP or SIP (Username / Password) Authentication for users.
Global IP and SIP Authentication
You can also configure and manage both IP and Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) Authentication for Customers and Carriers in Global IP Authentication or SIP User Authentication.
IP Authentication¶
When you enable IP Authentication, you link a customer switch's IP address to their account. This adds a layer of security by ensuring the calls are coming from a trusted source.
Newly added IP immediately marked as Blocked under IP Authentication
This occurs because call requests were sent from the new IP before it's authorized. As a result, ConnexCS fraud detection in the firewall blocked the unauthorised IP. Attempted calls from this IP won't get completed.
To resolve the blocked IP, go to Setup Advanced Firewall. Select the blocked IP, then delete it from the firewall. This unblocks the IP, but it will take up to 15 minutes for the change to become active in the switch.
See Threat Detection for more details.
Enable IP Authentication¶
To enable, click next to IP Authentication:
Click each tab to view the configuration details
- IP: Enter specific IPs or use CIDR notation to specify an entire subnet.
FQDN can be used for Ingress-only switches. -
Switch Direction: The available options are from the perspective of the customer switch (PBX, dialer, etc), and describe how that switch interacts with the ConnexCS switch. For switches that send and receive calls from ConnexCS, there should be separate entries for each direction.
Ingress: This switch receives calls from ConnexCS. (Note: When selected, this gives the option of using the FQDN rather than the switch IP.)Egress: This switch sends calls to ConnexCS. -
Channels: Set the maximum number of concurrent calls for this switch.
-
Flow Speed: Set the Calls Per Second (CPS) (0 = unlimited calls).
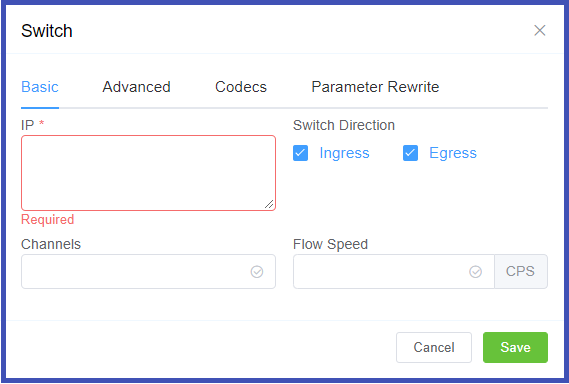
- Manufacturer and Version: These references fields allow you to enter the customer switch Manufacturer and Version, if required (these fields are not functional; they are informational only).
-
Protocol: Select the protocol for SIP (call signaling) and RTP (transport / audio).
UDP: SIP and RTP are unencrypted and transported over UDP.TCP: SIP is sent over TCP, RTP over UDP.TLS: SIP is sent over TLS (TCP), RTP over UDP.TLS & SRTP: SIP is sent over TLS (over TCP), RTP is encrypted with SRTP.SMPP: SMPP, for SMS, is not currently supported. -
Port: Default = 5060. If using TLS protocol, this should be set to 5061.
- Dial Pattern: The default selection is the industry standard.
- CLI Prefix, Tech Prefix, Force From: Do NOT Use these fields. Use the Parameter Rewrite tab to modify numbers.
- Username, and Password: Set when sending calls out (egress switch direction) to a remote system. Set this to allow the ConnexCS switch to operate as a client or UAC. Not typically recommended unless the customer has a very specialized system.
- Force NAT: Forces the switch to read the IP address the traffic was received from, not the IP in the SIP packet. (See Far-End NAT Traversal for more details on how ConnexCS handles NAT for SIP.)
- Intercept Reinvite: The only situation where this is recommended is when a customer's equipment doesn't support REINVITES. Enable this to correct issues with dropped calls by having ConnexCS respond to the INVITES, which can help keep calls up if they are being disconnected by the far-end switch.
- Outbound Proxy: Enter the IP address of a Proxy server for calls to route to before being sent to the carrier. This rewrites the UAC IP in the VIA field of the SIP header. This reduces management overhead as a customer only needs to authorize a single IP. Additionally, multiple addresses can be load-balanced using the AnyEdge system.
- Flags: Set CLI Authentication for situations where Accounts are unable to use Tech Prefix to differentiate customers using the same IP. CLI Tags is another way to do it.
- CLI Tags: Set the CLI Authentication and
Saveit for the required customer. Then go to Routing and put some CLI's in the allow list. For example, you have allowed 1234567 (CLI) in Routing, and add 1234578 (CLI) in the Customer. When this customer receives a call, it will be able to differentiate where the call (traffic) is from with the help of CLI Tags.
- CLI Tags: Set the CLI Authentication and
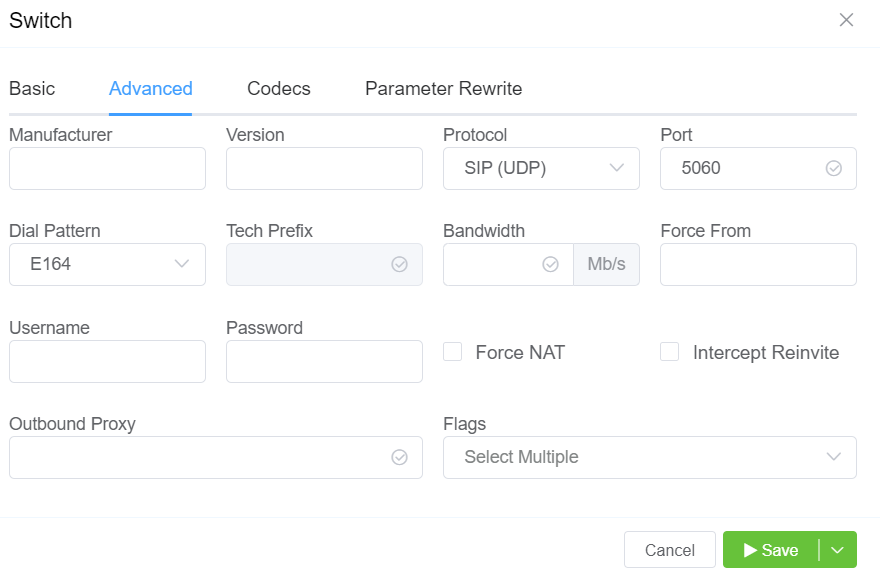
All Codecs are supported unless specifically set as "Restricted" here.
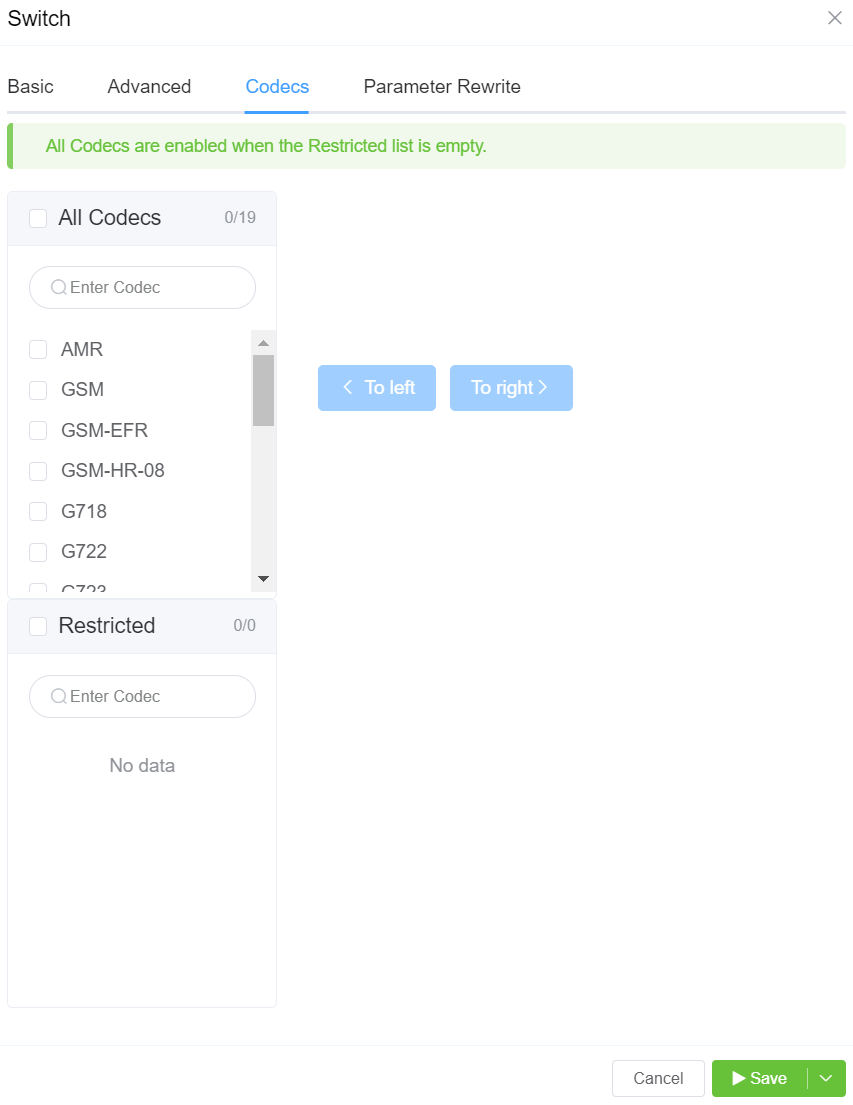
The Parameter Rewrite tab is used to manipulate data as it comes into the system.
It is most useful when you need to create automatic replacements for destination numbers or CLI, so a number is formatted in the appropriate E164 format.
- Click
+. - Type: Select the parameter to modify.
- Current: Enter the prefix for the destination number, or the CLI. You also have the option to generate a regular expression using
AI Generate Regular Expression. - New: Enter what should replace the current information.
- Use the Testing
Inputfield to verify if the replacement is working as expected. - Click
Savewhen done. - If a parameter rewrite is already created, you will have the ability to test it from the main tab.
Example: International calls coming in with a + should be replaced with a specific country code.
Note
Click here to view an interactive IP address and CIDR range visualizer.
SIP User Authentication¶
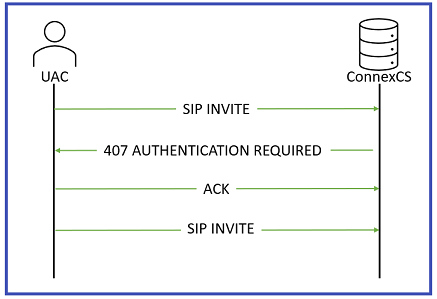
When you enable SIP Authentication, ConnexCS will reject the initial SIP INVITE with a "407 Authentication Required". This message includes a 'nonce' (a uniquely randomly generated hashed number). The customer switch will send appropriate authentication information to ConnexCS, which will connect the call.
Generic SIP Trace showing the Challenge Response:
sequenceDiagram
autonumber
Alice->>Bob: INVITE
Bob-->>Alice: 100 Trying
Bob->>Alice: 407 Proxy Authentication Required
Note over Alice,Bob: 407 contains nonce.
Note left of Alice: HASH(Combine Password + Nonce).
Alice->>Bob: INVITE (+ Auth Header)
Bob-->>Alice: 100 Trying
Note right of Bob: HASH(Combine Password + Nonce).
Note right of Bob: Compare Hashes - They Match.
Bob-->>Alice: 183 Ringing
Bob->>Alice: 200 OK (Connected)For call authentication we should have a Username and a Password. The Username and Password should get to the other side.
The Username is sent on Plain-text and the user (Alice) hashes the password. 407 Proxy Authentication contains a nonce. A nonce is a random String of which gets send over to Alice. Both Alice and Bob are aware of this random string. Authorization header is sent with the INVITE. Then Bob combines the password with the nonce and compares the nonce. If the hashes match, the call gets connected.
407 Proxy Authentication is a part of Challenge-Response and is necessary when you proceed with SIP User Auth. Also you can't have IP Authentication and User / Password Authentication work together
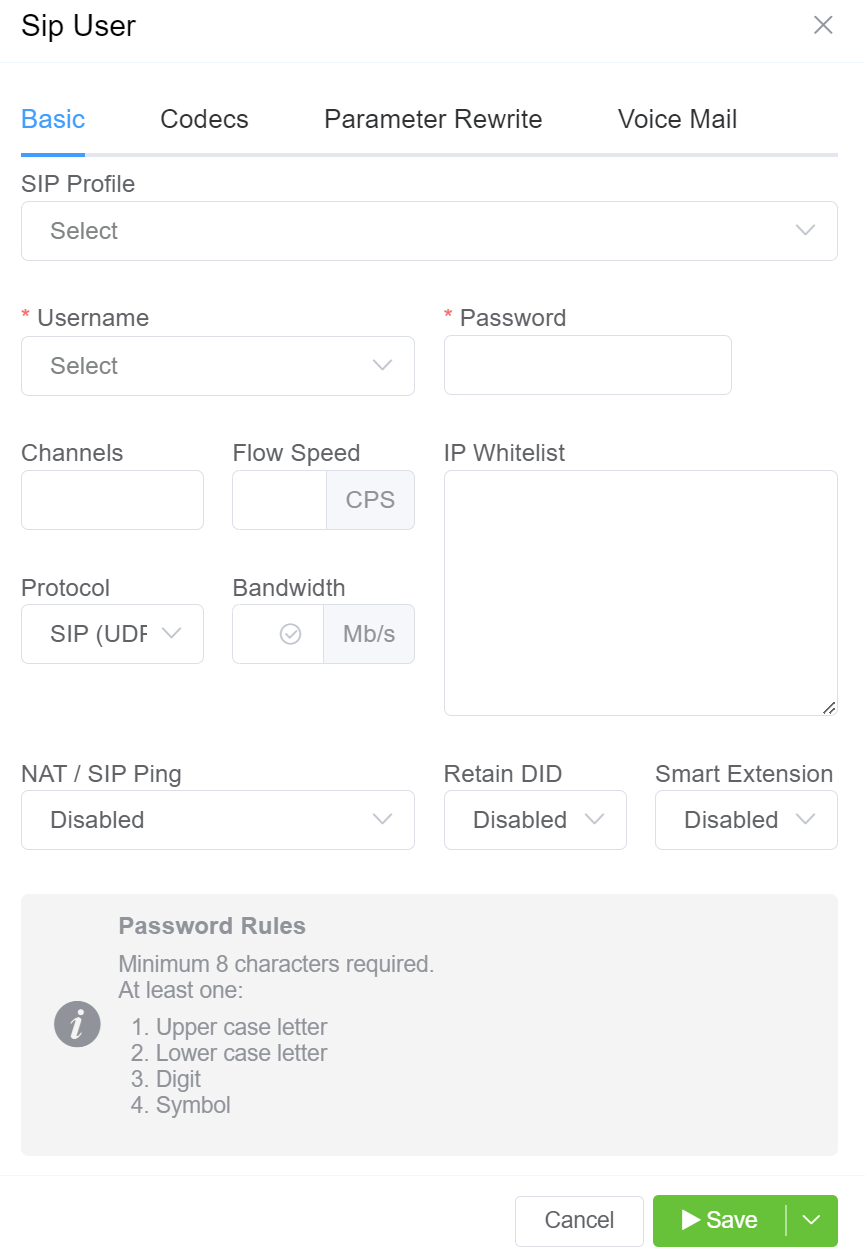
Enable SIP User Authentication¶
To enable, click next to SIP User Authentication:
Click each tab to view the configuration details
- SIP Profile: You can select the created SIP Profile here.
- Username: This will be the Username used for SIP authentication (must match configuration on the customer UAC). If the Customer has Internal Number Block set on the Main tab, you can only select the Username from available extensions. If a Username is already in use on the Account, they will get an error "Duplicate User Detected".
- Password: Must match with the configuration on the customer UAC.
- Channels: Set the maximum number of concurrent calls for this switch.
- Flow Speed: Set the Calls Per Second (CPS) (0 = unlimited calls).
-
Protocol: Select the protocol for SIP (call signaling) RTP (transport/audio).
UDP: SIP and RTP are unencrypted and transported over UDP.TCP: SIP is sent over TCP, RTP over UDP.TLS: SIP is sent over TLS (TCP), RTP over UDP.TLS & SRTP: SIP is sent over TLS (over TCP), RTP is encrypted with SRTP.SMPP: SMPP, for SMS, is currently not supported. -
IP Allow list: Enter specific IPs or use CIDR notation to specify an entire subnet.
-
NAT/SIP Ping: Set behavior of pings sent from ConnexCS back to the customer through their firewall to their UAC. This helps when there are remote agents connecting to the switch.
Disabled: No pings are sentEnabled: Send UDP pings every 60 seconds, helping to keep some longer calls (1800 or 3600 seconds) up.Enabled (Timeout): Send UDP pings every 60 seconds and disconnect the call (terminate registration) if the pings aren't returned. -
Retain DID: When you enable this, inbound calls will retain the destination number (DID), and the call is sent into the system, rather than using the SIP Username.
- Smart Extension: Calls are sent to the Class5, not Class4 infrastructure. This feature is currently in Alpha and is not recommended.
All Codecs are supported for the SIP user unless specifically set as "Restricted" here.

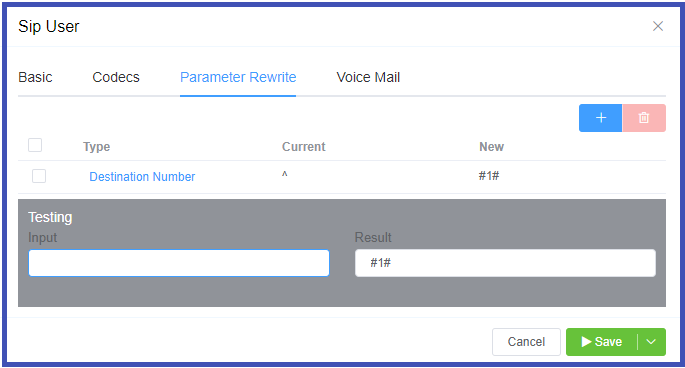
The Parameter Rewrite tab is used to manipulate data as it comes into the system. It is most useful when you need to create automatic replacements for destination numbers or CLI, so a number is formatted in the appropriate E164 format.
-
Click
+.
-
Type: Select the parameter to modify.
- Current: Enter the prefix for the destination number, or the CLI. You also have the option to generate a regular expression using
AI Generate Regular Expression. - New: Enter what should replace the current information.
- Use Testing
Inputfield to verify if the replacement is working as expected. - Click
Savewhen done. - If a parameter rewrite is already created, you will have the ability to test it from the main tab.
If you enable Voice Mail, you can set which email address receives messages, reset the Voicemail Password, and view and delete current messages.
See Voicemail for information on accessing Voicemail.
Reset SIP Password¶
Click the Password key next to the SIP user to reset the password.
You can also use Generate Password to generate a random and secure SIP password.
Make sure you Copy Text and provide this information for configuration, as this password can't be retrieved after it's set.
Customers using the Customer Portal can reset their SIP Passwords in Authentication.
SIP Password security
SIP passwords are needed for the SIP protocol, but they can present security risks for a provider.
You must configure them in ConnexCS when SIP authentication is setup, but they aren't available for providers to retrieve later.
Providers should generate a unique SIP password for each SIP user and send that to the customer. This gives the customer the responsibility of keeping track of the password and keeping it safe.
Additionally, the unique password will allow for traceability if the customer's system is ever compromised.
Send message to SIP Users¶
Use Send next to the SIP User to send a SIP message to the end device which will flash on the phone.
SIP Pings¶
Case 1: Normal SIP Ping
sequenceDiagram
autonumber
Alice->>Bob: INVITE (cseq 1)
Bob-->>Alice: 100 Trying
Bob-->>Alice: 183 Ringing
Bob->>Alice: 200 OK (Connected)
Alice->>Bob: ACK
Note over Alice,Bob: The call is active
Bob->>Alice: OPTIONS
Alice->>Bob: 200 OK
Note over Alice,Bob: The call has ended
Alice->>Bob: BYE
Bob->>Alice: 200 OKIn this case, Bob sends a message to Alice called OPTIONS and Alice sends back 200 OK. If 200 OK isn't sent, the call be get disconnected.
Case 2: Alice Disappears
Use Case for NAT/SIP Pings¶
Troubleshooting Scenario The Customer reports they can register and make outbound calls, but they're unable to receive inbound calls.
What's happening In a typical configuration, a packet is sent from the customer UAC out through a NAT/firewall, and then the packet gets delivered to the UAS:
graph LR
A(Customer switch) --> B(NAT/firewall)
B --> C(ConnexCS switch)
style A fill:#ECEFF1,stroke:#4051b5,stroke-width:4px
style B fill:#ECEFF1,stroke:#4051b5,stroke-width:4px
style C fill:#ECEFF1,stroke:#4051b5,stroke-width:4px- When a packet goes out, a hole gets punched in the firewall, and the source port gets recorded. When a packet returns on that port, the firewall knows to deliver back to the UAC.
- This works well when using TCP, which sends regular keep-alive packets.
- UDP doesn't send keep-alives (no connected state as with TCP). SIP does maintain a connected state, registration, but may have long periods of inactivity.
- Without regular traffic passing between UAS and UAC in the form of keep-alives/registration (a normal occurrence), NAT will eventually time out and shut down the connection.
- Enabling UDP or SIP pings can show the NAT/firewall that the signaling path is still valid and in use.